Enhancing Freeswitch Performance: Server Support and Optimization Techniques
Freeswitch is a powerful open-source telephony platform that provides flexibility and scalability for various communication needs. However, to fully harness its capabilities, it is crucial to optimize and support the Freeswitch server for optimal performance. This article explores effective techniques to enhance Freeswitch performance through server support and optimization. We will delve into key areas such as installation and configuration, troubleshooting common issues, and implementing optimization strategies.
Freeswitch Installation and Configuration :
Freeswitch is a versatile open-source telephony platform that offers a wide range of features and functionalities. To begin harnessing its power, it is essential to properly install and configure Freeswitch on your server. In this section, we will provide a step-by-step guide to help you through the installation and configuration process.
Step 1: Prerequisites
Before installing Freeswitch, ensure that your server meets the necessary requirements. This includes having a supported operating system, sufficient hardware resources (CPU, RAM, storage), and network connectivity.
Step 2: Download Freeswitch
Visit the official Freeswitch website (freeswitch.org) or the preferred distribution source to download the latest stable version of Freeswitch. You can choose to download the source code or pre-built packages, depending on your preference and system configuration.
Step 3: Installation
The installation process may vary depending on your operating system. Here, we will provide a general outline of the steps involved.
Extract the downloaded package or clone the source code to your desired location on the server.
Run the installation script or follow the instructions provided in the installation guide specific to your operating system.
The installation script will guide you through the necessary dependencies and libraries that need to be installed. Make sure to fulfill these requirements.
Step 4: Configuration
Once the installation is complete, it's time to configure Freeswitch for your specific needs. The configuration files are located in the conf directory within the Freeswitch installation directory.
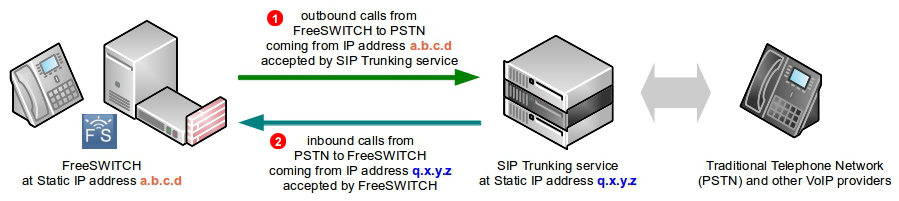
Start by configuring the vars.xml file, which contains variables for your environment, such as network settings, SIP trunks, and audio codecs. Customize these variables according to your requirements.
Next, modify the sip_profiles directory to configure SIP endpoints, gateways, and authentication settings.
Explore the other configuration files, such as extensions.xml for dial plan configuration and acl.conf.xml for access control lists, to tailor Freeswitch to your desired setup.
Step 5: Starting and Testing Freeswitch
Once you have completed the configuration, you can start the Freeswitch service. Use the provided command or service manager specific to your operating system to start Freeswitch.
To test the installation and basic functionality, you can use a softphone or SIP client to connect to your Freeswitch server. Create a user account, configure your softphone with the appropriate credentials, and attempt to make a test call.
Troubleshooting Freeswitch:
Freeswitch, like any complex telephony system, may encounter issues that can affect its performance and call quality. Troubleshooting is an essential skill for administrators to diagnose and resolve problems promptly. In this section, we will explore common issues that can arise in Freeswitch and provide strategies for effective troubleshooting.
Connectivity Problems:
- One of the most common issues in Freeswitch is connectivity problems, which can result in failed or dropped calls. To troubleshoot connectivity issues:
- Check network connectivity and ensure that the server has proper access to the internet and required ports are open.
- Verify firewall settings to allow traffic to and from the Freeswitch server.
- Monitor network bandwidth and latency to identify any network-related bottlenecks.
Audio Distortions:
- Audio distortions can degrade call quality and make conversations difficult. To troubleshoot audio issues:
- Verify the audio codecs used by Freeswitch and ensure compatibility with the client devices or service providers.
- Check audio devices and configurations on the server and endpoints.
- Monitor network quality metrics, such as packet loss and jitter, to identify potential causes of audio distortions.
Call Drops:
- Call drops can be frustrating for users and may occur due to various reasons. To troubleshoot call drop issues:
- Examine Freeswitch logs for any error messages or warnings related to call disconnections.
- Investigate potential hardware or software issues, such as inadequate server resources or configuration conflicts.
- Verify the configuration settings related to timeouts, session limits, and call routing to identify possible causes.
Configuration Errors:
- Configuration errors can lead to unexpected behavior and functionality gaps. To troubleshoot configuration issues:
- Review the configuration files and compare them against the documentation or recommended settings.
- Double-check variables, paths, and syntax within the configuration files for accuracy.
- Utilize the Freeswitch command-line interface (CLI) to test and validate configurations in real-time.
Diagnostics and Logging:
- Freeswitch provides extensive diagnostic capabilities and logging mechanisms. To troubleshoot issues effectively:
- Enable detailed logging and review log files to identify any error messages, warnings, or anomalies.
- Use diagnostic tools, such as the Freeswitch CLI or third-party monitoring applications, to gather real-time information on calls, sessions, and system performance.
- Utilize packet capture tools to inspect network traffic and analyze SIP signaling for troubleshooting complex issues.
Remember, troubleshooting Freeswitch requires a systematic approach and a good understanding of the underlying telephony principles. It is crucial to document and analyze symptoms, test different scenarios, and gradually eliminate potential causes until the issue is identified and resolved. Additionally, it's recommended to leverage the Freeswitch community resources, including forums and mailing lists, to seek advice and guidance from experienced users and developers.
Server Monitoring and Performance Metrics:
Monitoring Freeswitch performance server is crucial for ensuring its stability, identifying bottlenecks, and proactively addressing potential issues. In this section, we will explore server monitoring techniques and performance metrics that can help administrators optimize their Freeswitch environment.
Real-Time Monitoring:
Real-time monitoring allows administrators to track the server's performance and health in real-time. It provides immediate visibility into system resources, call statistics, and network connectivity. Some commonly used monitoring tools for Freeswitch include:
FusionPBX: A web-based interface that provides real-time call monitoring, resource utilization, and system status.
Nagios: A popular open-source monitoring system that can be customized to monitor Freeswitch servers and send alerts for critical events.
Telegraf: A data collection agent that can be integrated with InfluxDB and Grafana to build comprehensive monitoring dashboards.
Log Analysis:Logs provide valuable insights into the behavior and performance of your Freeswitch server. By analyzing logs, you can identify errors, warnings, and patterns that might indicate underlying issues. Some key logs to monitor include:
Freeswitch Event Log: Captures events related to calls, registrations, and system activities.
System Log: Contains system-level logs that can provide information about hardware, software, and network events.
Performance Metrics:Tracking performance metrics allows administrators to assess the health and efficiency of their Freeswitch server. Some important performance metrics to monitor include:
CPU Utilization: Measures the percentage of CPU resources consumed by Freeswitch processes. High CPU utilization may indicate resource contention or inefficient configurations.
Memory Usage: Monitors the memory consumption of the server. High memory usage can lead to performance degradation or even crashes.
Network Traffic: Monitors incoming and outgoing network traffic to identify potential bottlenecks or abnormal patterns.
Call Statistics: Tracks metrics such as call volume, call duration, and call success rate to gain insights into overall call quality and system performance.
Alerting and Notifications:Setting up alerts and notifications is crucial to promptly address any critical events or performance degradation. Configure thresholds for specific metrics and receive alerts via email, SMS, or other notification mechanisms when those thresholds are exceeded. This enables proactive actions and timely troubleshooting.
Historical Data and Trend Analysis:Storing historical performance data allows for trend analysis and capacity planning. By analyzing long-term data, administrators can identify usage patterns, anticipate resource requirements, and make informed decisions to optimize server performance.
It is important to establish a comprehensive monitoring strategy that aligns with your specific needs. Combine real-time monitoring, log analysis, performance metric tracking, and alerting to ensure the ongoing health and performance of your Freeswitch server. Regularly review the collected data and adjust your configurations as needed to optimize resource utilization and deliver a smooth user experience.
Security Considerations and Best Practices:
Ensuring the security of your Freeswitch server is vital to protect sensitive data, prevent unauthorized access, and maintain the integrity of your telephony system. In this section, we will explore essential security considerations and best practices to safeguard your Freeswitch environment.
Secure Network Configuration:
- Employ firewalls and network segmentation to restrict access to your Freeswitch server. Only allow necessary ports and protocols for communication.
- Implement secure remote access mechanisms, such as Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), to ensure encrypted and authenticated connections to your server.
User Authentication and Authorization:
- Enforce strong passwords for all user accounts and require regular password updates.
- Implement two-factor authentication (2FA) to add an extra layer of security to user logins.
- Assign appropriate permissions and access levels to users based on their roles and responsibilities.
Encryption:
- Utilize Transport Layer Security (TLS) or Secure Real-time Transport Protocol (SRTP) to encrypt signaling and media streams, respectively. This ensures the confidentiality and integrity of communications.
- Regularly update and renew SSL/TLS certificates to maintain secure communication channels.
Regular Software Updates:
Keep Freeswitch and all associated software components up to date with the latest security patches and bug fixes. Regularly check for updates from the official Freeswitch website or your distribution source.
Secure Media Handling:
- Implement media handling policies to prevent unauthorized access or interception of voice data.
- Utilize secure codecs and encryption methods for media streams to protect against eavesdropping.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention:
- Deploy intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) to monitor and block suspicious network activities.
- Regularly review IDS/IPS logs and configure alerting mechanisms to promptly respond to potential threats.
Regular Backup and Disaster Recovery:
- Maintain regular backups of your Freeswitch configurations, databases, and critical data. Store backups securely in off-site locations.
- Establish a disaster recovery plan to ensure business continuity in the event of system failures or security breaches.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, enhancing the performance of your Freeswitch server requires a combination of server support, optimization techniques, and robust security measures. By following best practices for installation, troubleshooting, optimization, monitoring, and security, administrators can maximize the potential of Freeswitch and provide a reliable and efficient telephony system.
During the installation and configuration phase, ensuring that prerequisites are met and following proper installation procedures lays the foundation for a stable Freeswitch environment. Troubleshooting common issues such as connectivity problems, audio distortions, and call drops allows administrators to maintain optimal call quality and user satisfaction.
Leveraging Open Source in ICT





